
Architects play an essential role in designing buildings that tackle sustainability. Through well-thought-out strategies and buy-in from important players, these initiatives can make a big difference in helping shrink the environmental footprint during the construction and lifetime of a building.
The impact of architecture on the environment is evident as the global push for more sustainable thinking continues. Quite simply, poorly designed, and constructed buildings use more energy. In the field of architecture, sustainability architects are the ones who oversee the design and construction of buildings while considering how the structure of the building will ultimately affect the environment.
Their role is to create buildings that people enjoy spending time in and serve the function they were built for. During the construction and the lifetime of the building, architects consider ways to minimize the impacts on the environment.
For sustainable design to become a reality, the building requires the buy-in of the design team and the building occupiers. For now, many architects and building developers are taking promising steps towards sustainability initiatives.
Here’s how architects are approaching building design and construction while tackling sustainability:
Green building materials
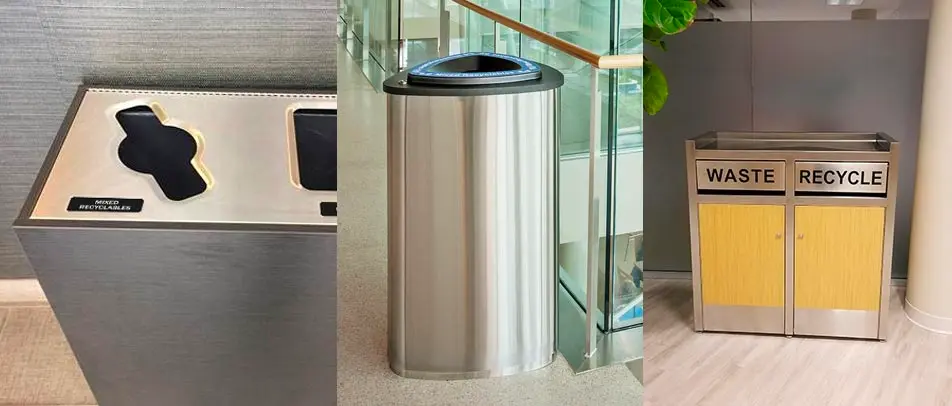
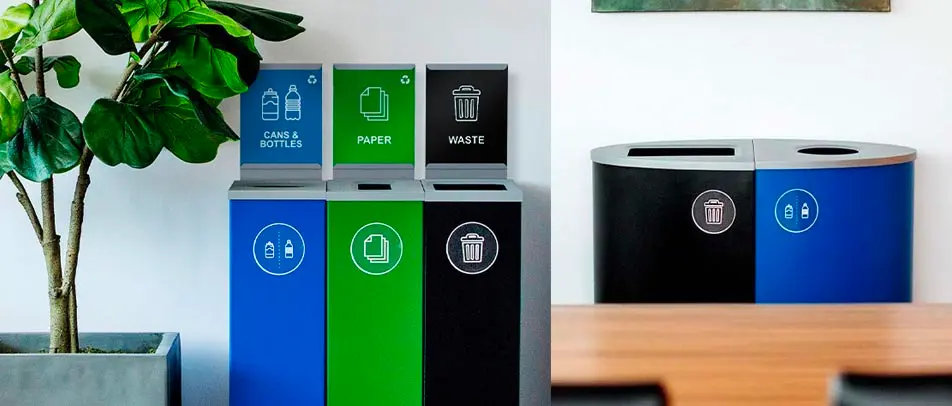
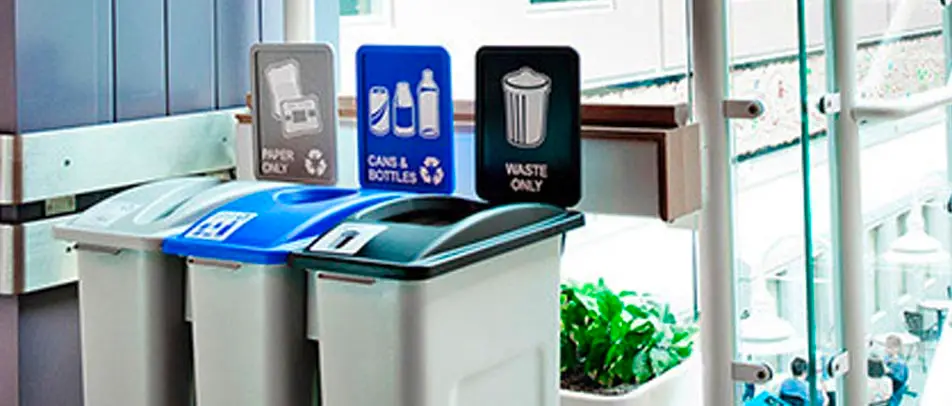
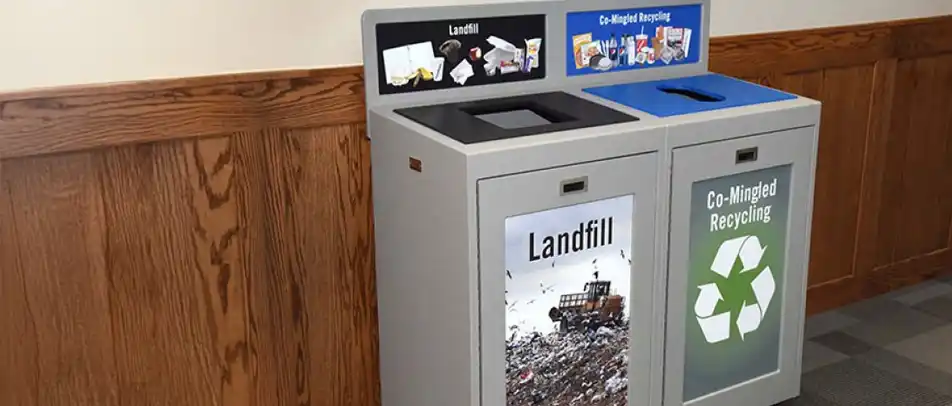
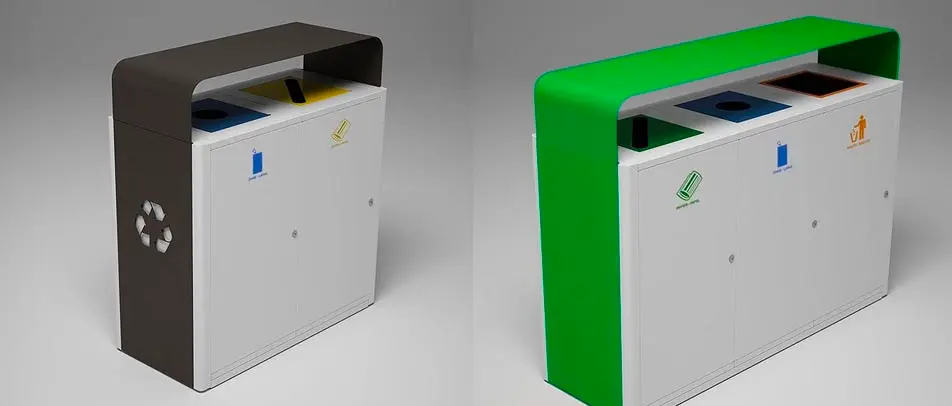
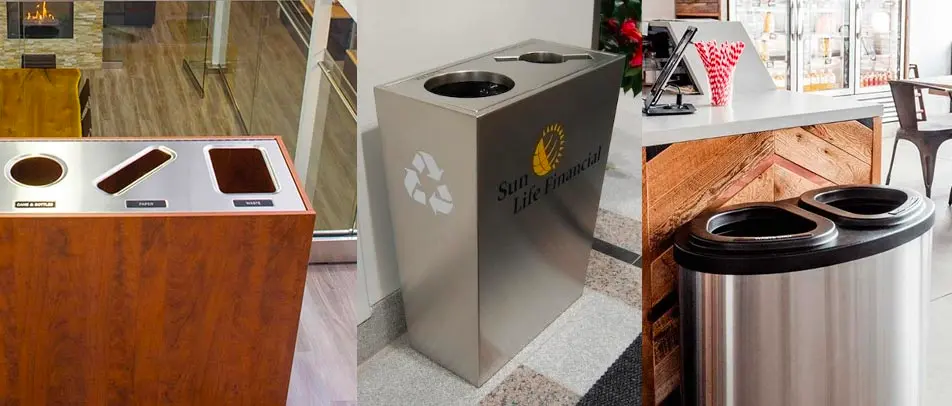
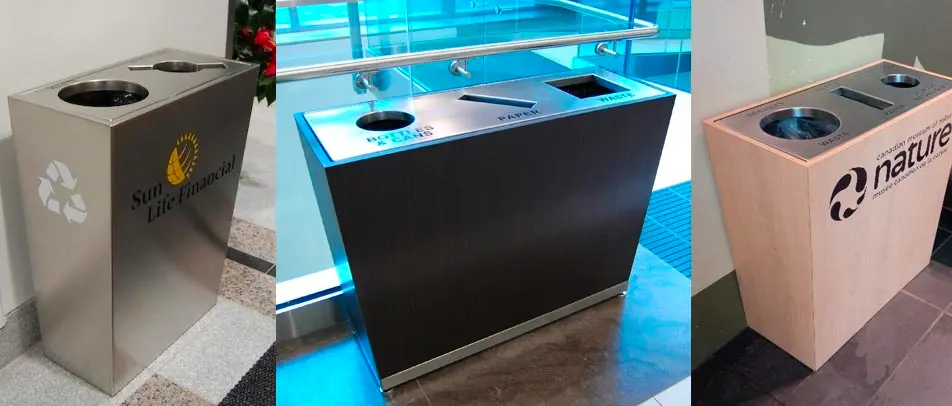
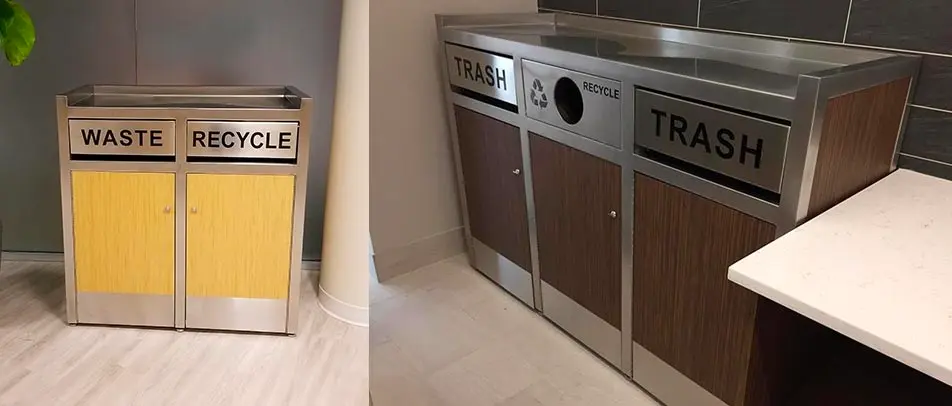
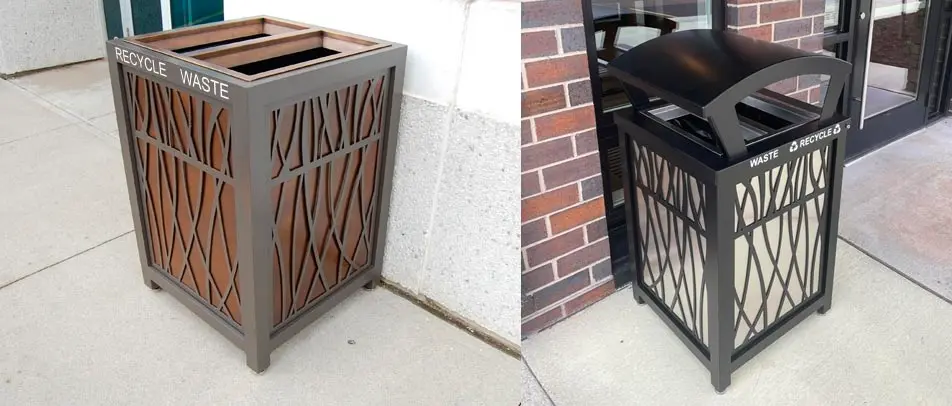
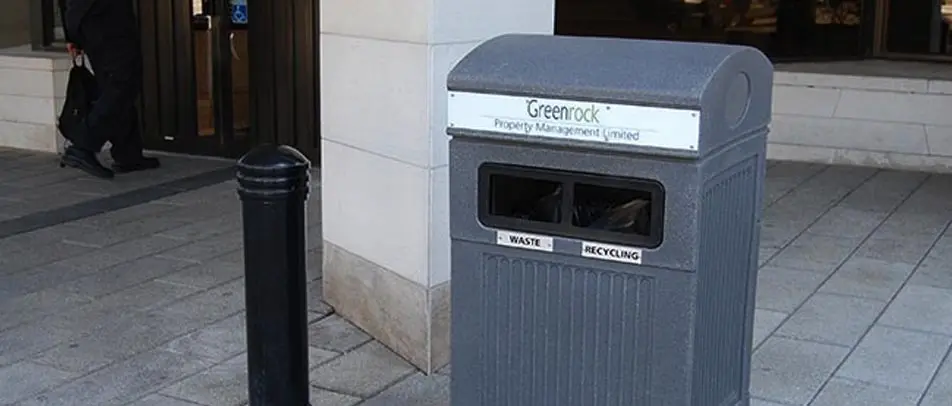
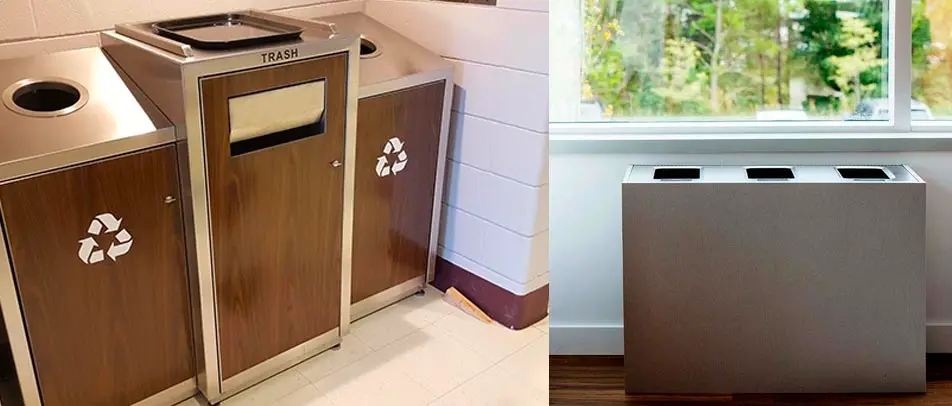
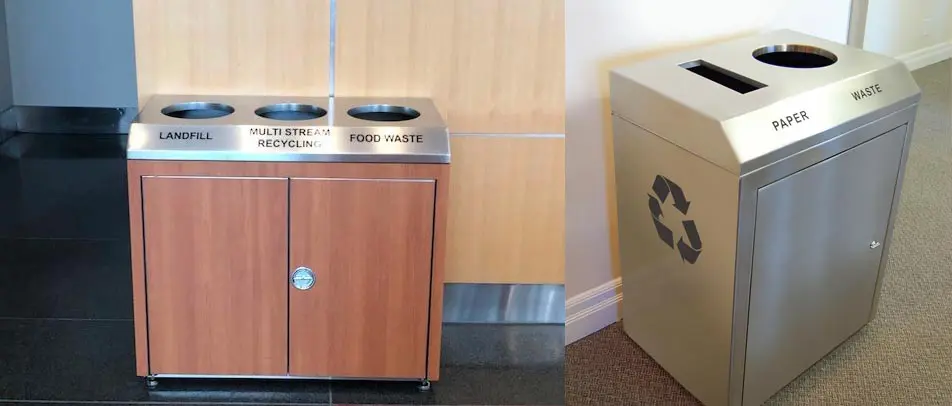
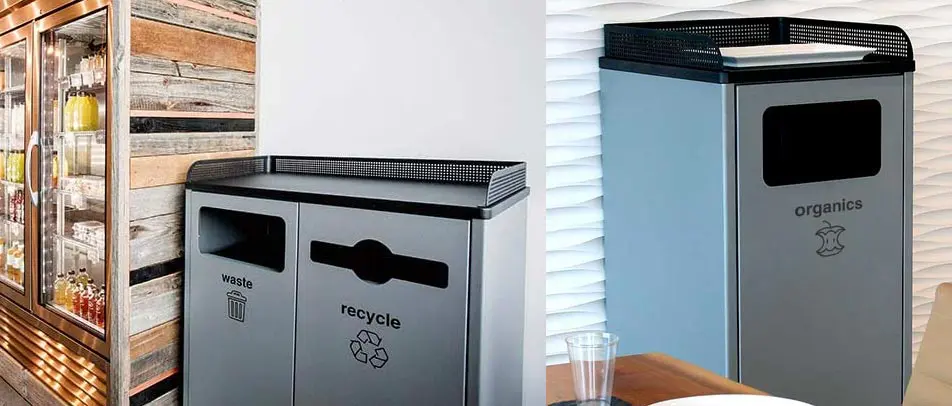
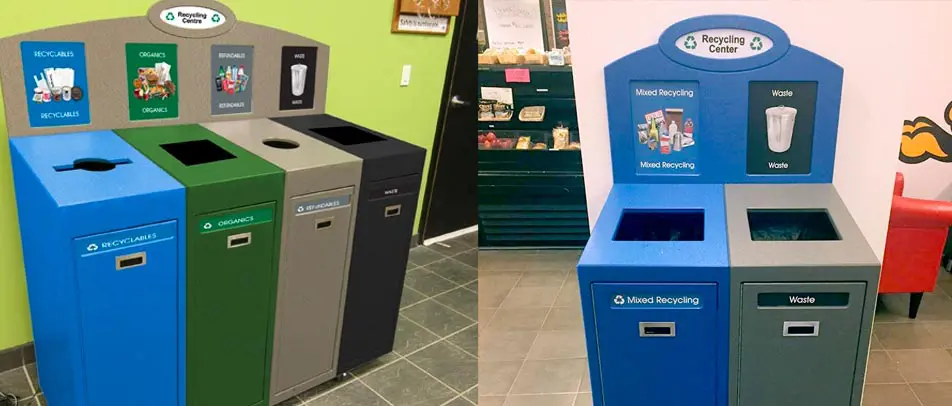
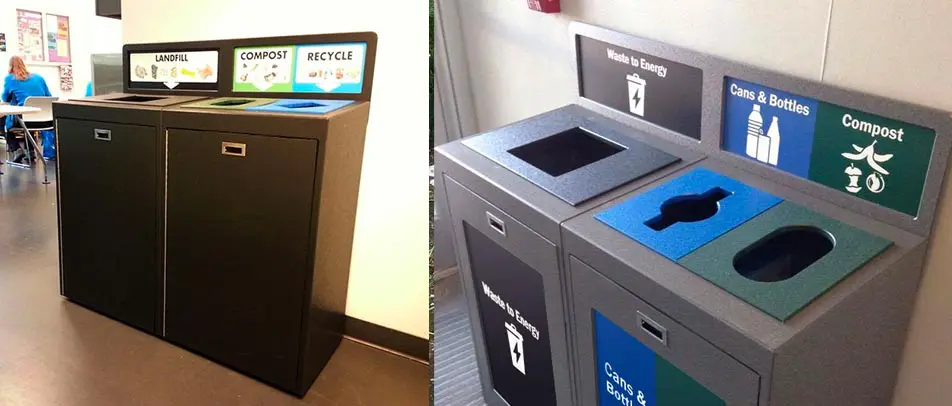
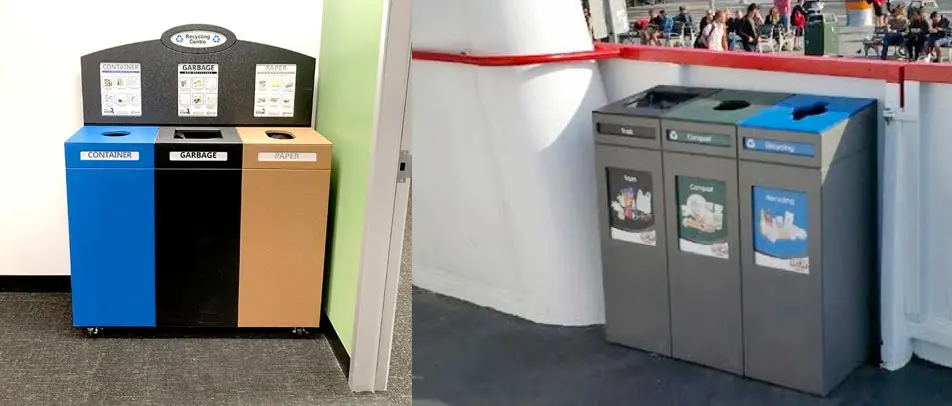
While no building material is perfect, some are more sustainable than others. Buildings must have the right type of trash and recycle bin to support efforts of using recycled materials for the construction of buildings. In addition, reusing materials when designing a building can go a long way to reducing the environmental impact. For example, researchers are creating a type of concrete that is made by recycled plastics and trash.
Architects can limit the purchasing of new materials created for the project to minimize waste. Consider that new materials need to be harvested, refined, manufactured, and then shipped. This process alone requires a lot of energy and creates a large carbon footprint.
Architects can also make it a priority to purchase steel, wood, concrete, and other materials from companies that use sustainable manufacturing techniques or recycled materials. Although concrete remains a popular material for building construction, the production of concrete releases high amounts of greenhouse gases.
Using wood continues to retain many advantages over other industrial materials such as steel or concrete. Wood takes less energy to process into usable construction materials. Trees also absorb CO2 as they get older, forests are renewable and can ensure biodiversity for wildlife.
Passive sustainable design
This type of sustainable design strategy focuses on taking advantage of natural elements to reduce the need for artificial energy sources. Whether it’s sunlight, wind, or other sources, these buildings can harness these forces to use for energy without requiring mechanical equipment.
Passive design depends mostly on the way the building is oriented. Whenever possible, passive strategies and low-energy systems are used to manage energy demand.
Passive ventilation – uses naturally occurring airflow patterns to introduce outdoor air into the building. Architects can design buildings to enhance these airflows. For example, cross ventilation uses windows on both sides of the room to create a current of air that moves across the room.
Passive ventilation is most effective when the climate outside is comfortable for most months of the year without being mechanically cooled or heated.
Daylighting – this strategy involves maximizing the distribution of natural daylight to reduce the need for artificial electric lighting. This method depends on the building’s orientation. Architects design buildings so that the rooms that require the most daylight face north or south.
Architects can use windows, skylights, solar tubes, transparent doors, mirrors, and other surfaces that are reflective to direct natural light in other areas of the building.
The added benefit is that natural daylight is also better for the health and wellness of the building’s occupiers.
Passive heating – when the sun strikes a building, this strategy relies on the building materials absorbing and reflecting solar radiation. This strategy uses the natural sun to absorb the heat and heat the building when the sun is absent.
Passive cooling – these strategies involve storing the cool temperatures in the night to moderate warm daytime temperatures. Through shading, blocking solar resources, and cross ventilation, the building, can be kept cool.
Active sustainable design
Architects strategize with mechanical and electrical engineers to fit the building with high-efficiency HVAC, plumbing, and electrical solutions.
Active sustainable design uses technologies to allow the building to produce electricity on its own. These technologies include solar panels, heat recovery, renewable energy sources. The energy used is purchased to keep buildings comfortable for those occupying it.
The key to maximizing the efficiency of active systems is to consider how they will work together with passive systems.























































































 Three Ways to Engage Teams and Clients to Maximize Your Recycling Program Engagement
Three Ways to Engage Teams and Clients to Maximize Your Recycling Program Engagement  How to Integrate Accessibility Into Your Sustainability Planning
How to Integrate Accessibility Into Your Sustainability Planning  Why Park Benches Can Promote Workplace Well-Being
Why Park Benches Can Promote Workplace Well-Being 
